Dynamics 365 Product Catalog Overview
A product catalog is a collection of products and services that an organization sells and provides to customers. It includes pricing information. In Dynamics product catalog not only includes a list of the products that an organization sells but also defines different pricing based on the customer types like retail and wholesale, and quantity levels on how a product will be sold.
● Define a hierarchical structure of product families and products that have configurable properties (attributes). These attributes help you reduce the number of product stock keeping units (SKUs) that are required to maintain your product catalog.
● Sell individual products or group them into bundles and kits. A bundle or a kit is a collection of products that’s sold as a single unit. Product bundling is useful for grouping products in such a way that customers will benefit from the full line of products. It also lets you offer discounts on bundled products.
● Define related products in the system. (For example, these related products might be substitute, cross-sell, up-sell, or accessory products.) The related products for a product are shown to sales agents as suggestions when they add the product to an opportunity, quote, order, or invoice.
● Define multiple pricing and discounting models. You can also use custom pricing instead of the Dynamics 365 system pricing to calculate prices when you associate a product or bundle with an opportunity, quote, order, or invoice. Additionally, you can select whether to apply discounts for products at the per-unit level or the line level.
● Specify whether the price level (that is, the price list) should be automatically set for an opportunity,
quote, order, or invoice, based on the user’s sales territory relationship.
● Specify localized values for some product properties (attributes) to make the product names and
descriptions available in user-preferred languages.
Product catalog components
The Dynamics 365 product catalog consists of four components:
● Unit groups: A unit group defines how a product is packaged for sale. Among other values, it defines the units of measure that the product or service is sold in.
● Products: A product represents the type of product that a company might keep in inventory, a product that’s custom-built, or a service that’s provided to a customer.
● Price lists: A price list is a set of prices that are charged for products or services under specific circumstances or based on the customer type. For example, an organization might have multiple price lists to accommodate seasonal variations, specials, or the different markets that the organization sells.
● Discount lists: A discount list lets organizations offer products or services at different prices, depending on the quantity that’s bought. For example, a small vendor that buys five TVs to sell in its store
might pay $350.00 per TV, whereas a large vendor that buys 500 TVs to sell in multiple locations
might pay $300.00 per TV. Of all the components in the preceding list, only discount lists aren’t required.
All other components must be set up for any organization that will use the product catalog. Because of the way that units, discounts, and prices are linked, it’s important that you create the components in a product catalog in the following order.

● Dynamics 365 Sales: The product catalog stores the goods and services you sell to your customers;
so, they can be used as line items on opportunity, quote, order, and invoice records. Different price
lists ensure that the pricing is correct based on the customer type.
● Dynamics 365 Customer Service: The product catalog can be used by different service records,
such as case(complaints), knowledge articles, and entitlement records. For example, knowledge articles can be associated with products from the catalog to make it easier to find articles based on a type of product.
● Dynamics 365 Field Service: The product catalog is used on work orders to represent the products
and services being provided as part of the work order. Products from the product catalog can be
automatically converted into customer assets, which represent equipment at customer locations that
can be serviced by your organization. As a technician uses a product or performs a service, they enter the work into the Field Service Mobile App. Used products and performed services can be invoiced to customers based on the applicable price list or entitlement. Used products can be deducted from inventory levels either in the Field Service inventory module or with any (ERP) system like FinOps, SAP.
● Dynamics 365 Marketing: The product catalog can be used to help target marketing campaigns and
customer journeys. It can also be used to help in customer segmentation.
● Dynamics 365 Project Operations: The product catalog can be used to add product line items to
project opportunity, project quote, and order contracts.
With a dedicated product catalog that can function stand alone or be integrated with ERP applications, such as Dynamics 365 FinOps (Finance & Operations) or with any other ERP like (SAP), you can quickly build sales quotes by adding products directly from the product catalog. Automated pricing options can update pricing details automatically.
For basic products inventory requirements, we can use the inventory module which comes with Dynamics 365 Field Service. For more complex inventory and pricing requirements we can integrate with ERP systems like FinOps.
Products, Product Bundle & Family:
Products in the product catalog represent the individual items and services that an organization sells to
its customers. A product might be used to define something physical like a printer, a shirt, or a kitchen
appliance. Alternatively, it might be used to define a service that’s provided, like a disposal service or
consultation fee. Products can be defined individually, as families, or as bundles. Before you set up
products, we recommend that you define any discounts that can be applied based on the quantities of a
product that are sold.
A bundle is a collection of products that are sold as a single unit. From within a bundle, users can see all
the products that are included in the bundle.
Here are some of the scenarios where product bundling can be useful:
● You want to pair a top-selling product with a less popular product.
● You want to group products in such a way that customers will get more benefit from the full line of
products. Examples digital camera that comes with lenses
Product families make it easier for sales staff to find products and services in a product catalog. They let
you create and categorize similar products together, based on commonalities between them.
Product properties
Another advantage of product families is that you can define properties to help distinguish products. For
example, a property can be used to offer size or color options for shirts that belong to the same family.
Properties can be defined at the family level only when the family is in a draft or revision state. To define
properties, select the Add New Property button. Any child products, bundles, or child families will
automatically inherit the properties from their parent family.
Product lifecycle:

Unit groups
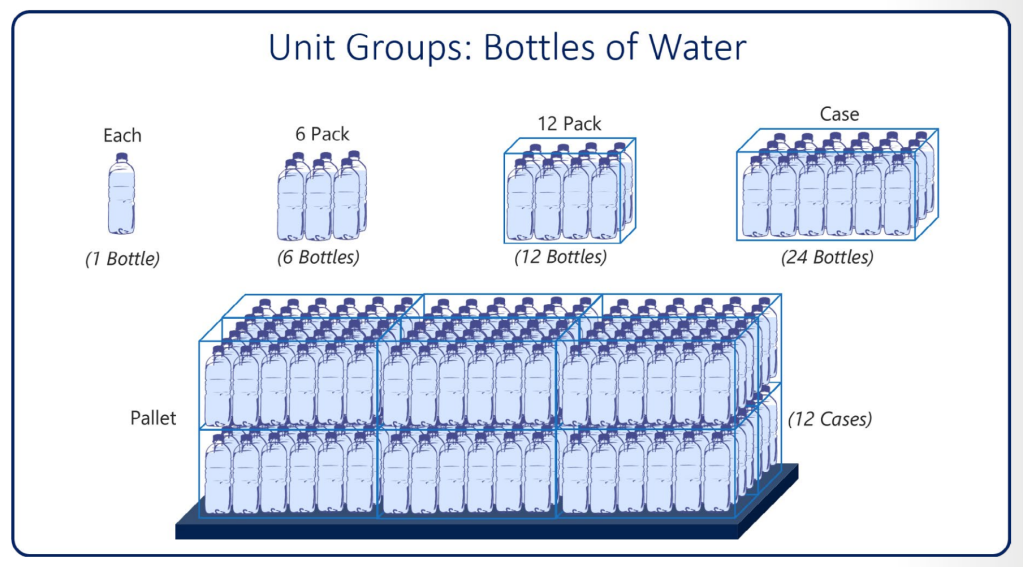
Before products can be defined an organization must define units to define how its products can be sold.
Units are the quantities or measurements that you sell your products or services in. For example, an
organization that sells water bottle supplies might sell seeds in individual bottle, packs that have multiple bottles, or case that have multiple bottles. Each one of those selling options represents a unit. A unit group is a collection of these different units.
Price lists
Organizations might sell products and services to many different types of customers. Depending on the
type of customer, different pricing options might be used. For example, retail pricing for individual
consumers is generally higher than wholesale pricing for distributors, because distributors typically buy in
larger quantities and more often. For each product that an organization sells, it might have to define
different levels of pricing, depending upon the customer type and region.
Assigning price lists to territories
Some organizations might use different pricing options, depending on geographic regions or territories.
The product catalog can accommodate these scenarios by letting you add default price lists for territories. When a price list that’s defined as the default list for a territory offers any new items in that territory, like an opportunity, the default price list is used. A different price list can then be selected as needed.
Discount lists
Discount lists aren’t required, but they can be used to set up discounts according to the volume of
products that’s purchased. After a discount list is set up, it can be associated with individual items on the
price lists that the organization uses. Because an organization can use many different price lists, many
different pricing scenarios can be accommodated. On a price list, a discount can be applied to a price list
item only for quantities that are in a specified range.
Currencies and currency management
Organizations that do business in multiple countries/regions often need to handle multiple currencies.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 supports the use of multiple currencies in an organization and by individual
users. Therefore, users can perform financial transactions like opportunities, quotes, orders, and invoices
in multiple currencies.
Three components help support the Dynamics 365s multi-currency solution:
● Base currency- The base currency is the currency that other currencies are quoted in.
● Transaction currency- The transaction currency is the currency that’s used for a specific transaction.
● Exchange rates- An exchange rate represents the number of units of a transaction currency that
equals one unit of the base currency.
Base currency
When Dynamics 365 is installed in an organization, a default currency for the organization is defined. The base currency provides a way to review and report on all monetary transactions that occur in a single currency, regardless of how those transactions were entered. After the base currency is defined for an organization, it can’t be changed.
A default currency isn’t required. But if a default currency isn’t specified, users must select a currency
every time they create a new financial transaction. If a default currency is specified, it will be used unless a
different currency is specified for a specific transaction.
Transaction currency
Different currencies can be created for an organization and used on a transaction-by-transaction basis.
These currencies are referred to as transaction currencies.
Transaction currencies let you perform these tasks:
● Select the currency that you want to define and transact opportunities, quotes, orders, and invoices in.
● Define currency exchange rates relative to the base currency.
● Define transaction currencies, and define exchange rates to associate the base currency with those
transaction currencies.
● Capture the value of a transaction in both the base currency and the transaction currency in all
financial transactions.
● Define product price lists for each currency.
Hope this blog post given some idea about product catalog (overview). I have shared from my point of view & as per my product knowledge. Happy to hear from others if I have missed anything.

Leave a comment